How to Use Metformin Liquid for Type 2 Diabetes?
- admin
- June 6, 2025
- 5:41 am
- No Comments

Managing type 2 diabetes involves a multifaceted approach, blending lifestyle changes with pharmaceutical support to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Among the cornerstone medications prescribed for this condition is metformin—a trusted, first-line treatment that improves insulin sensitivity and curbs glucose production in the liver.
While most people are familiar with metformin in its tablet form, fewer are aware of its liquid counterpart: metformin hydrochloride oral solution.
This formulation is particularly beneficial for children, elderly patients, or those with dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), offering a more flexible option for precise dosage titration.
Additionally, liquid metformin may be easier to digest and absorb for certain patients, potentially improving adherence and therapeutic outcomes.
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, this version maintains the same active compound and therapeutic benefits as the tablet, but in a more patient-friendly format.
For many, this alternative marks a small but significant shift in personalized diabetes management.
In this Article You Learn:
- What Is Metformin Liquid and How Does It Work?
- Who Can Benefit from Metformin Liquid?
- How to Take Metformin Liquid Correctly
- Dosage Guidelines for Metformin Liquid
- Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
- Storage and Handling of Metformin Liquid
- Monitoring Your Progress on Metformin Liquid
- Conclusion
What Is Metformin Liquid and How Does It Work?
Metformin liquid, also known as metformin hydrochloride oral solution, is an effective antihyperglycemic agent used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
You may want to reduce daily calorie intake to treat type 2 diabetes the natural way.
It helps regulate blood sugar levels through several mechanisms, each targeting a different aspect of glucose metabolism:
Decreases Hepatic Glucose Production:
Reduces the amount of glucose produced and released by the liver, particularly during fasting periods.
Reduces Intestinal Absorption of Glucose:
Slows down the uptake of glucose from the gastrointestinal tract, minimizing spikes in blood sugar after meals.
Improves Insulin Sensitivity:
Enhances the ability of muscle and fat cells to absorb and utilize glucose, lowering insulin resistance.
Lowers Basal and Postprandial Glucose Levels:
Provides balanced blood sugar control throughout the day, both during fasting and after food intake.
Supports Long-Term Glycemic Control:
Ideal for Patients with Swallowing Difficulties:
Offers an accessible alternative for those who cannot tolerate tablet forms, improving medication adherence.

Who Can Benefit from Metformin Liquid?
Metformin liquid is especially useful for specific populations who may face challenges with traditional tablet forms.
Its formulation offers flexibility and ease of administration, making diabetes management more accessible for the following groups:
Children Aged 10 and Above:
Approved by regulatory bodies for pediatric use, the liquid form is ideal for younger patients who often struggle with swallowing large tablets. It ensures they still receive consistent and effective treatment.
Elderly Patients:
As people age, physical limitations such as reduced swallowing ability or dry mouth can make pill ingestion difficult. The liquid version eliminates this barrier, ensuring older adults can maintain their prescribed medication regimen comfortably.
Individuals with Dysphagia:
Patients with medical conditions like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or esophageal disorders often experience dysphagia. The liquid form offers a safe and manageable alternative to solid pills.
Patients Requiring Precise Dosing:
Liquid metformin enables fine-tuned dose adjustments, essential for individuals who are starting treatment, have fluctuating glucose levels, or need gradual titration to minimize side effects and optimize glycemic control.
How to Take Metformin Liquid Correctly?
To ensure metformin liquid delivers its full therapeutic benefits, proper usage is essential.
Take with Meals:
Metformin is best absorbed when taken with food, which also significantly reduces common gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, bloating, or diarrhea. Clinical trials, including those published in the Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, have shown that co-administration with meals improves gastrointestinal tolerance without compromising efficacy.
Use the Provided Measuring Device:
Always use the dosing syringe or cup provided with the medication to ensure precision. Household spoons are unreliable and can lead to over- or under-dosing, potentially impacting blood sugar control. For example, a variation of just 2 mL in a 500 mg/5 mL solution can alter the dose by 200 mg—enough to affect blood glucose levels.
Follow Your Healthcare Provider’s Instructions:
Stick closely to your prescribed dose and timing. Skipping doses or self-adjusting can lead to glucose instability. Even small changes in dose should only be made under medical supervision to avoid hypoglycemia or ineffective treatment.
Dosage Guidelines for Metformin Liquid
Dosage of metformin liquid can vary based on individual factors such as age, weight, kidney function, and blood glucose control.
However, there are general dosing guidelines to help initiate and adjust therapy safely:
Starting Dose for Adults:
Typically, treatment begins with 500 mg (5 mL) twice daily or 850 mg (8.5 mL) once daily, taken with meals to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Starting low and going slow helps the body adapt.
Dose Adjustments:
Physicians may increase the dose in 500 mg (5 mL) increments each week or 850 mg (8.5 mL) every two weeks, depending on the patient’s glucose readings and tolerance. This gradual titration helps minimize common side effects like nausea and diarrhea, as supported by findings in the Diabetes Care journal.
Maximum Adult Dose:
The recommended upper limit is 2,550 mg (25.5 mL) per day, divided into multiple doses with meals to optimize absorption and maintain steady plasma levels.
Pediatric Dosing (Ages 10+):
Children usually start at 500 mg (5 mL) twice daily, with a maximum dose of 2,000 mg (20 mL) daily, split into two meals. Dosing in children must be carefully monitored to ensure safety and efficacy.
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Common side effects of metformin liquid include:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, and a metallic taste.
Management tips:
-
- Take the medication with meals to minimize stomach upset.
- Start with a lower dose and gradually increase as directed by your doctor.
- If symptoms persist, consult your healthcare provider.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Long-term use may lead to decreased vitamin B12 levels.
Management tips:
-
- Regular monitoring of vitamin B12 levels.
- Supplementation if necessary, as advised by your doctor.
- Lactic acidosis: A rare but serious side effect characterized by muscle pain, difficulty breathing, and unusual tiredness.
Management tips:
-
- Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of lactic acidosis.
- Inform your doctor about any kidney or liver issues before starting metformin.
Storage and Handling of Metformin Liquid
Proper storage of metformin liquid is essential to preserve its stability, potency, and safety.
Refrigeration:
The oral solution should be stored in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). This temperature range helps maintain the medication’s chemical integrity and ensures that it continues to work effectively throughout its use.
Shelf Life:
Once opened, the liquid formulation should be used within 14 days. After this period, its effectiveness may decrease, and using expired medication could compromise blood glucose control.
Avoid Freezing:
Never freeze the solution. Freezing can lead to the separation of ingredients and degradation of the active compound, rendering the medication ineffective or unsafe.
Keep Out of Reach of Children:
Always store the bottle in a secure location, away from children and pets. Accidental ingestion can lead to serious side effects, including dangerously low blood sugar levels or lactic acidosis, a rare but serious complication.
By following these storage guidelines, patients can ensure the medication remains safe and effective for the duration of its use.
Monitoring Your Progress on Metformin Liquid
Regular monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, especially when using medications like metformin liquid.
Tracking key health indicators helps determine whether the medication is working as intended and ensures that potential complications are caught early.
-
Blood Glucose Levels:
Frequent self-monitoring—whether through finger-stick tests or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)—helps assess how your body is responding to metformin. Daily readings allow adjustments to be made in real-time, particularly in response to meals, activity, or stress.
-
HbA1c Tests:
This lab test, typically done every 3 to 6 months, reflects your average blood glucose levels over the previous 8 to 12 weeks. It’s a reliable long-term indicator of glycemic control. According to the American Diabetes Association, a target HbA1c of below 7% is generally recommended for most adults.
-
Kidney Function Tests:
Since metformin is cleared by the kidneys, tests like serum creatinine and eGFR are essential to ensure the drug is not accumulating to unsafe levels. Reduced kidney function may require dose adjustments or discontinuation to avoid the rare but serious risk of lactic acidosis.
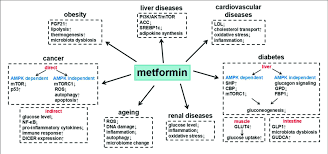
Takeaway
Metformin liquid offers a valuable alternative for managing type 2 diabetes, always club it with the best supplements to lower blood sugar.
This is particularly for those who struggle with swallowing tablets or need flexible, precise dosing adjustments.
Whether you are a parent managing pediatric metformin dosing for your child or an adult seeking a more tolerable formulation, this oral solution can simplify your diabetes care routine.
To get the most out of your treatment, it is essential to know how to take metformin liquid with meals—a practice that helps minimize stomach upset while improving absorption.
Using the provided dosing syringe ensures accuracy, which is vital for maintaining stable glucose levels. Don’t forget the importance of monitoring HbA1c and checking blood sugar levels regularly to track progress.
And because metformin is cleared through the kidneys, make sure to schedule routine kidney function tests. Proper storage of metformin hydrochloride oral solution—refrigerated and never frozen—also ensures its effectiveness.
With careful use and consistent follow-up, liquid metformin becomes a powerful ally in your journey toward better glycemic control and overall well-being.
References: