How to Use a Glucometer for Daily Blood Sugar Management?
- admin
- January 8, 2026
- 7:37 pm
- No Comments
Managing blood sugar on a daily basis is one of the most important habits for anyone living with diabetes or prediabetes.
A glucometer may look like a small device, but it plays a big role in helping you understand what is happening inside your body.
Each reading tells a story about how your food choices, activity levels, medications, stress, and sleep are affecting your glucose levels.
When used correctly and consistently, a glucometer becomes more than just a testing tool—it becomes a guide for making smarter, healthier decisions every single day.
This article by bestdietarysupplementfordiabetics.com is designed to help you confidently use a glucometer as part of your daily routine.
You will learn what a glucometer is, how it works, when to check your blood sugar, and how to interpret the numbers you see on the screen.
We shall also cover common mistakes, practical accuracy tips, and how to use your readings to improve long-term blood sugar control.
Whether you are newly diagnosed or looking to fine-tune your routine, this step-by-step guide will help you turn daily testing into meaningful blood sugar management.
Points Covered in this Article
- What Is a Glucometer and How It Works
- Why Daily Blood Sugar Monitoring Is Important
- Supplies You Need Before Testing
- Preparing Yourself for an Accurate Reading
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Glucometer
- Best Times of Day to Check Blood Sugar
- Understanding Blood Sugar Numbers
- How Food Affects Your Glucometer Readings
- The Impact of Exercise, Stress, and Illness
- Recording and Tracking Your Blood Sugar Data
- Common Glucometer Mistakes to Avoid
- Tips to Improve Accuracy and Comfort
- Using Your Readings to Adjust Daily Habits
- When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
- Conclusion
What Is a Glucometer and How It Works?
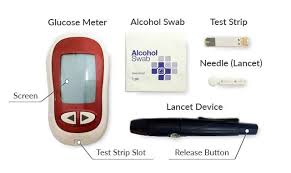
A glucometer is a portable medical device used to measure the amount of glucose in your blood. It works by analyzing a tiny drop of blood, usually taken from the fingertip.
The blood sample is placed on a disposable test strip, which reacts chemically with the glucose in your blood.
The glucometer reads this reaction and displays your blood sugar level on the screen, typically within a few seconds.
Most modern glucometers are easy to use, lightweight, and designed for home testing.
Some models store readings automatically, while others connect to mobile apps that track trends over time.
Regardless of the model, the goal is the same: to give you fast, reliable information about your current blood sugar level so you can make informed decisions throughout the day.
Why Daily Blood Sugar Monitoring Is Important?
Daily blood sugar monitoring helps you stay aware of how well your diabetes management plan is working.
Blood sugar levels can change throughout the day due to meals, physical activity, medications, emotional stress, and even lack of sleep.
Without regular testing, these fluctuations can go unnoticed.
Checking your blood sugar regularly allows you to catch high or low levels early, before they turn into serious problems.
It also helps you understand patterns—such as whether your blood sugar rises after certain meals or drops after exercise.
Over time, this awareness empowers you to make adjustments that keep your levels within a healthier range and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Supplies You Need Before Testing
Before using a glucometer, it is important to have all the necessary supplies ready. These typically include:
- A glucometer compatible with your test strips
- Test strips specific to your glucometer model
- A lancing device and sterile lancets
- Soap and water or alcohol swabs
- A sharps container for used lancets
- A logbook or digital app for recording readings
Having everything prepared ahead of time makes testing quicker, more comfortable, and more accurate. Always store your supplies in a clean, dry place and check expiration dates on test strips regularly.
Preparing Yourself for an Accurate Reading
Preparation plays a much bigger role in blood sugar testing than many people realize. Even small oversights can lead to inaccurate readings, which may affect daily management decisions.
The first and most important step is washing your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water.
Warm water helps improve blood flow to your fingers, making it easier to obtain a good blood sample, while soap removes any traces of food, sugar, oils, or lotions that could falsely raise or lower your reading.
After washing, dry your hands completely, as moisture can dilute the blood sample and interfere with test strip accuracy.
If you prefer using an alcohol swab, make sure your finger is fully dry before testing. Testing on damp skin can cause stinging and may affect the reading.
Once your hands are clean and dry, choose a finger that feels comfortable and free from tenderness.
It is best to use the sides of your fingertips rather than the center, as this area has fewer nerve endings and is less painful.
Avoid using the same finger or exact spot repeatedly, since doing so can lead to soreness, bruising, or thickened skin that makes future testing more difficult.
Rotating fingers regularly allows each fingertip time to heal and helps maintain consistent blood flow.
Before lancing, you can gently massage your hand or lower it below heart level for a few seconds to encourage circulation.
Taking these simple preparatory steps may only take a minute, but they significantly improve comfort, accuracy, and confidence in your blood sugar readings.
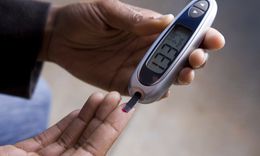
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Glucometer
Using a glucometer becomes second nature once you follow a consistent routine. Here is a clear step-by-step process:
- Wash and dry your hands thoroughly.
- Insert a new test strip into the glucometer.
- Load a fresh lancet into the lancing device.
- Adjust the depth setting on the lancet if needed.
- Prick the side of your fingertip, not the center.
- Gently squeeze or massage the finger to form a drop of blood.
- Touch the blood drop to the test strip.
- Wait for the glucometer to display your reading.
- Record the result along with the time and any notes.
- Dispose of the used lancet safely.
Following these steps each time ensures consistency and builds confidence in your daily testing routine.
Best Times of Day to Check Blood Sugar
The timing of your blood sugar checks can reveal different insights about your health. Common testing times include:
- First thing in the morning before eating (fasting level)
- Before meals
- One to two hours after meals
- Before physical activity
- Before bedtime
- Whenever you feel symptoms of high or low blood sugar
Your healthcare provider may recommend specific testing times based on your condition, medications, and goals.
Sticking to a regular schedule helps you compare readings accurately and spot trends more easily.
Understanding Blood Sugar Numbers
Blood sugar readings are usually displayed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). While target ranges vary from person to person, general guidelines often suggest lower numbers before meals and slightly higher numbers after eating.
Rather than focusing on a single reading, it is more helpful to look at patterns over time. Occasional highs or lows happen, but consistent trends may signal the need for changes in diet, activity, or medication. Understanding your numbers helps you respond calmly and confidently instead of feeling discouraged.
>>> Want to Learn How I “Treated My Diabetes Naturally” at Home??? Click Here to Find Out <<<
How Food Affects Your Glucometer Readings?
Food has a direct and often immediate effect on your blood sugar levels, which is why glucometer readings can change noticeably before and after meals.
Carbohydrates have the strongest impact because they break down into glucose during digestion. Refined carbohydrates and sugary foods—such as white bread, pastries, sweetened cereals, soft drinks, or candy—tend to cause faster and higher blood sugar spikes. So, low glycemic diet is recommended for diabetics.
For example, you may notice a sharp rise in your reading one to two hours after eating a slice of white bread or drinking a sugary beverage.
Proteins and fats usually affect blood sugar more slowly and steadily. A meal with lean protein, such as grilled chicken or eggs, may cause little to no immediate rise in glucose.
Healthy fats from foods like nuts, avocado, or olive oil can slow digestion, leading to a more gradual blood sugar increase. Mixed meals also matter.
For instance, eating rice alone may raise your blood sugar quickly, while pairing rice with vegetables and protein may result in a smaller, slower rise.
By checking your blood sugar before eating and again after meals, you can see how specific foods affect your body.
These insights help you adjust portion sizes, choose better food combinations, and time meals more effectively.
Over time, your glucometer becomes a practical feedback tool that guides smarter, more balanced eating habits (such as Whole30 Diet for blood sugar control).
The Impact of Exercise, Stress, and Illness
Exercise, stress, and illness can all significantly influence your blood sugar levels, sometimes in unexpected ways.
Physical activity often lowers blood sugar because working muscles use glucose for energy more efficiently.
For example, a brisk walk after a meal may lead to a noticeable drop in your reading, while longer or more intense workouts can cause blood sugar to fall even further.
Testing before and after exercise helps you understand how different activities affect you and whether you need a snack or adjustment.
Stress and illness tend to have the opposite effect.
Emotional stress, lack of sleep, infections, or fever can trigger the release of stress hormones that raise blood sugar levels, even if you are eating less than usual.
Regular monitoring during stressful periods or when you are unwell helps you recognize these changes early.
This allows you to respond appropriately by staying hydrated, adjusting meals, resting, or contacting your healthcare provider if levels remain elevated.
Recording and Tracking Your Blood Sugar Data
Recording and tracking your blood sugar readings is just as important as testing itself because it gives context to the numbers you see.
You can log your results in a notebook, a spreadsheet, or a mobile app—what matters most is consistency.
Along with the reading, note the time of day, what you ate, any physical activity, medications taken, and how you were feeling.
For example, writing “140 mg/dL, 2 hours after lunch, pasta meal” helps explain why the number is higher.
Similarly, noting “90 mg/dL after a 30-minute walk” shows how exercise affected your levels.
Over time, these details reveal patterns that single readings cannot. You may notice higher morning readings, spikes after certain foods, or drops after workouts.
Sharing these records with your healthcare provider allows for more accurate adjustments to diet, medication, or daily routines.
Consistent tracking turns daily testing into meaningful insights that support long-term blood sugar control and better decision-making.
Common Glucometer Mistakes to Avoid
Some common mistakes can lead to inaccurate readings, including:
- Testing with unwashed hands
- Using expired or damaged test strips
- Not applying enough blood to the strip
- Reusing lancets too often
- Storing supplies improperly
Being aware of these errors helps you avoid frustration and ensures your readings truly reflect your blood sugar levels.
Tips to Improve Accuracy and Comfort
To make testing easier and more reliable:
- Use the side of your fingertip to reduce pain
- Rotate fingers regularly
- Keep your hands warm to improve blood flow
- Replace lancets frequently
- Store your glucometer and strips as instructed
Small adjustments can greatly improve your daily testing experience.
Using Your Readings to Adjust Daily Habits
Your glucometer readings are most valuable when you use them to guide everyday decisions. They help you understand what is working and what needs adjustment.
For example, if you consistently see high readings one to two hours after dinner, it may signal that your portions are too large or that the meal contains too many refined carbohydrates.
In this case, reducing portion size, adding more vegetables, or pairing carbohydrates with protein may help bring numbers down.
On the other hand, if your readings tend to drop after physical activity, such as feeling shaky or seeing low numbers after a long walk or workout, you may benefit from having a small snack before exercising. A combination of carbohydrates and protein can help prevent these lows.
The goal of monitoring is not perfect numbers every day, but steady improvement over time.
Each reading offers useful feedback that helps you adjust meal timing, activity levels, and daily habits, leading to better and more consistent blood sugar control.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider?
It is important to contact your healthcare provider whenever your glucometer readings show patterns that concern you.
If you notice frequent high blood sugar readings over several days, especially after following your usual diet and medication routine, it may indicate that your treatment plan needs adjustment.
Likewise, repeated low readings, particularly those that occur without warning, should never be ignored. For example, if your blood sugar drops below your usual range after meals or during normal daily activity, your medication or meal timing may need review.
You should also reach out if you experience unexplained changes, such as sudden spikes during fasting periods or wide fluctuations from day to day.
Physical symptoms are another key reason to call, including dizziness, confusion, excessive thirst, frequent urination, shakiness, or extreme fatigue.
Bringing your glucometer records to your appointment allows your healthcare provider to see patterns, identify triggers, and make precise changes.
Early communication helps prevent complications and supports safer, more effective blood sugar management.
Conclusion
Using a glucometer for daily blood sugar management is one of the most practical and empowering habits you can develop.
It transforms invisible internal changes into clear, actionable information that helps you take control of your health.
By learning how to test correctly, choosing the right times to check, understanding your numbers, and tracking patterns over time, you turn daily monitoring into a powerful decision-making tool.
A glucometer is not just about numbers on a screen—it is about awareness, confidence, and prevention.
Each reading teaches you something new about how your body responds to food (such as opting for a gluten free diet), movement, stress, and rest.
With consistent use and thoughtful interpretation, daily blood sugar monitoring supports better choices, fewer surprises, and stronger long-term health.
When used wisely, your glucometer becomes a trusted partner in managing blood sugar and living well every day.
References: